Nearly a century after the De Beers Company put diamonds on the map with its 1930s marketing campaign featuring popular movie stars,1 demand for mined diamonds has plummeted, as more couples opt for less expensive and ethically sourced diamond alternatives.
According to the IDEX Diamond Index, diamond prices have fallen more than 36% since their peak in spring 2022:

If you are shopping for a diamond alternative, there are several types of “fake diamonds” available at multiple price points, including lab-grown diamonds, which have the same chemical and physical properties as mined diamonds and are technically not fake diamonds at all — but are skyrocketing in popularity.2
In this post, we’ll explore popular diamond alternatives so you can make an informed decision before you purchase one:
- Cubic zirconia
- Lab-grown diamonds
- Moissanite
- White spinel
- Composite diamond
- Fools diamond
- Replica / travel diamond
- What's the best diamond alternative?
How to tell if a diamond is real
FAQs about fake diamond vs real diamonds
Here's a quick side-by-side comparison of natural diamonds with the “fake diamonds” covered in this post:
| Natural diamonds | Cubic zirconia | Lab diamonds | Moissanite | White spinel | |
| Composition | 99.95% carbon (0.5% trace elements | Made of zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) in a lab | 100% carbon | Naturally occuring or made in a lab from silicon carbide | Magnesium and aluminum — MgAl₂O₄ is their chemical formula |
| Mohs Hardness Scale rating | 10 | 8-8.5 | 10 | 9.25 | 8 |
| Appearance | Tend to have a more clear, white sparkle and can range in color from yellowish to white | Sparkles more than a real diamond, though it typically reflects rainbow light | Graded on the same color scale as natural diamonds | Doubly refractive quality which causes them to give off a rainbow “disco ball” light | Comes in a variety of colors based on the presence of trace elements |
| Retail value | $4,330 (based on Brilliant Earth pricing above) | Most cubic zirconias are available for less than $30 | $1,160 (based on Brilliant Earth pricing) | $525 (based on Brilliant earth pricing) | $300 to $3000 per carat, depending on the vibrancy and rarity of the color, though some stones sell for less than $20 |
| Resale value | Most diamonds are worth about 50% or less of their retail value | Virtually no resale value | Most fetch as little as 20% of their retail value, if you can resell them at all | Virtually no resale value | Spinel isn’t as widely known as other gemstones, so you may have more difficulty selling it or getting a fair price if you do |
Types of fake diamonds
For each of the fake diamond options below, we will cover:
- Composition
- Color
- Hardness
- Brilliance
- Conductivity
- Retail price
- Resale value
While diamond prices can vary widely between retailers and based on the quality and size of the diamond, for the purpose of this article, we will compare the price of each type of fake diamond to the price of a 1-carat round diamond from online jeweler Brilliant Earth with the following attributes:
- Cut: Super ideal
- Color: D
- Clarity: VS2
A representative from Brilliant Earth told me these specs would be most comparable to those of a moissanite stone, one of the fake diamonds on this list. Brilliant Earth prices this natural diamond at $4,330 as of July 2024:

Cubic zirconia
The cheapest type of fake diamond on this list, cubic zirconia are primarily used in inexpensive fashion jewelry and in general aren’t recommended for engagement rings or fine jewelry pieces because of their low durability.
Cubic zirconia are denser and heavier than diamonds. A 6.5-mm diamond is about 1 carat, while a 6.5-mm cubic zirconia is about 1.7 carats.
Here’s how they stack up against mined diamonds:
| Cubic zirconia | Mined diamonds | |
| Composition | Made of zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) in a lab | 99.95% carbon (0.5% trace elements that don’t impact the diamond’s composition but can impact its color) |
| Color | Cubic zirconia is not graded on the diamond scale (based on color, cut, clarity, carat size) but may be graded on an overall quality scale from 1A to 5A (with 5A being the highest quality) | Colorless diamonds are considered the most valuable — the less yellow their appearance, the higher their value (with the exception of colored diamonds) |
| Hardness (based on the Mohs Scale of Hardness) | 8-8.5 | 10 |
| Brilliance | 2.15 to 2.18 refractive index, which means cubic zirconia may appear to sparkle more than a real diamond, though it typically reflects rainbow light | 2.42 refractive index; Tend to have a more clear, white sparkle; Singly refractive |
| Conductivity | Can become electrically conductive as it approaches temperatures of 500°C | Diamonds cannot conduct electricity |
| Retail value | Most cubic zirconias are available for less than $30 | $4,330 (based on Brilliant Earth pricing above) |
| Resale value | Virtually no resale value | Most diamonds are worth about 50% or less of their retail value |
Learn more about the differences between cubic zirconia and diamonds.
Lab-grown diamonds
In 2023, 46% of engagement ring center stones sold were lab-grown, according to a survey by wedding website The Knot.3
The primary difference between natural and lab diamonds is that lab diamonds are manufactured in a lab using one of two methods:
- High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT)3: Applies high temperatures and pressure to a small diamond seed crystal to make a diamond grow around the seed
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)3: A diamond seed crystal is placed in a chamber filled with carbon gas and heated to a high temperature; then, a microwave beam creates a plasma cloud that deposits carbon precipitation onto the diamond seed, forming a diamond
Here’s how they compare to mined diamonds:
| Lab-grown diamonds | Mined diamonds | |
| Composition | 100% carbon; Natural diamonds contain trace amounts of nitrogen and other elements, while lab-made diamonds do not. | 99.95% carbon (0.5% trace elements that don’t impact the diamond’s composition but can impact its color) |
| Color | Lab diamonds are graded on the same color scale as natural diamonds (with colorless stones being the most valuable) | Colorless diamonds are considered the most valuable — the less yellow their appearance, the higher their value (with the exception of colored diamonds) |
| Hardness (based on the Mohs Scale of Hardness) | 10 | 10 |
| Brilliance | Same as natural diamonds | 2.42 refractive index; Tend to have a more clear, white sparkle; Singly refractive |
| Conductivity | While most lab diamonds cannot conduct electricity, it is possible to introduce trace materials during the production process to make them conduct electricity | Diamonds cannot conduct electricity |
| Retail value | $1,160 (based on Brilliant Earth pricing) | $4,330 (based on Brilliant Earth pricing above) |
| Resale value | Most fetch as little as 20% of their retail value, if you can resell them at all | Most diamonds are worth about 50% or less of their retail value |
A 1-carat lab-grown diamond from Brilliant Earth with the same attributes as the mined diamond above costs $1,160, a price difference of more than $3,000:

Learn more about the similarities and differences between lab diamonds and natural diamonds.
Moissanite
Moissanite has risen in popularity by 10% since 2019, according to The Knot survey, with 3 in 10 couples who selected a non-diamond stone choosing moissanite over other gemstones or diamond alternatives.
Next to lab diamonds, they are the most similar option to natural diamonds:
| Moissanite | Mined diamonds | |
| Composition | Moissanite was discovered as a naturally occurring mineral, though most moissanite sold today is a lab-created gemstone made of silicon carbide | 99.95% carbon (0.5% trace elements that don’t impact the diamond’s composition but can impact its color) |
| Color | Most are colorless, though some moissanites exhibit a faint green, yellow, or gray hue, especially in sunlight | Colorless diamonds are considered the most valuable — the less yellow their appearance, the higher their value (with the exception of colored diamonds) |
| Hardness (based on the Mohs Scale of Hardness) | 9.25 | 10 |
| Brilliance | 2.65 refractive index; doubly refractive quality which causes them to give off a rainbow “disco ball” light | 2.42 refractive index; Tend to have a more clear, white sparkle; Singly refractive |
| Conductivity | 25% more thermally conductive than diamonds and can conduct electricity | Diamonds cannot conduct electricity |
| Retail value | $525 (based on Brilliant earth pricing) | $4,330 (based on Brilliant Earth pricing above) |
| Resale value | Virtually no resale value, though you may be able to sell them independently on sites like Facebook Marketplace or Craigslist, or to a local consignment shop | Most diamonds are worth about 50% or less of their retail value |
Brilliant Earth classifies moissanite into two categories based on quality — Premium (comparable to a G or H on the diamond color scale) and Super Premium (comparable to diamonds in the D-F range).4
This 6.5 mm super premium moissanite is comparable to the Brilliant Earth natural diamond, but costs nearly $4,000 less:

Learn more about moissanites vs. diamonds.
White spinel
Spinel is a gemstone that comes in a variety of colors, including white. The color of the stone is affected by trace elements — for example, the presence of chromium creates red spinel, while iron and cobalt create blue spinel. Spinel is available in both natural and lab-grown forms, though it is primarily sold by lesser-known and independent retailers on sites like Etsy.
While white spinel can be used in place of a diamond, it generally reflects light in a less obvious way and is fairly distinguishable from a real diamond:
| Moissanite | Mined diamonds | |
| Composition | Spinels are made up of magnesium and aluminum — MgAl₂O₄ is their chemical formula | 99.95% carbon (0.5% trace elements that don’t impact the diamond’s composition but can impact its color) |
| Color | Comes in a variety of colors based on the presence of trace elements | Colorless diamonds are considered the most valuable — the less yellow their appearance, the higher their value (with the exception of colored diamonds) |
| Hardness (based on the Mohs Scale of Hardness) | 8 | 10 |
| Brilliance | 1.712 – 1.736 refractive index (varies by color); spinel is singly refractive like a diamond | 2.42 refractive index; Tend to have a more clear, white sparkle; Singly refractive |
| Conductivity | Spinels exhibit electrical conductivity at high temperatures | Diamonds cannot conduct electricity |
| Retail value | $300 to $3000 per carat, depending on the vibrancy and rarity of the color, though some stones available on Etsy are worth less than $20 | $4,330 (based on Brilliant Earth pricing above) |
| Resale value | Natural spinel's supply is somewhat limited, so its rarity means it’s likely to retain value over time; however, spinel isn’t as widely known as other gemstones, so you may have more difficulty selling it or getting a fair price if you do | Most diamonds are worth about 50% or less of their retail value |
There were no white spinels available for sale on Brilliant Earth’s website, so we pulled several white spinels available from Etsy, which range in price from $15.75 to $135.
There were no exact 1-carat white spinels for sale, so we pulled one that was close to a carat and examples that were slightly higher and lower in carat weight:



Composite diamond
Composite diamonds aren’t a type of fake diamond but rather a cluster of diamonds set closely together to resemble a larger stone. Composite diamonds can be made up of mined diamonds, lab-grown diamonds, or diamond simulants like moissanite and cubic zirconia.
Jewelry with composite diamond designs are typically less expensive than those with larger carat center stones.
For example, this ½ carat composite diamond ring from Zales is on sale for $799.99 (originally priced at $1,229):

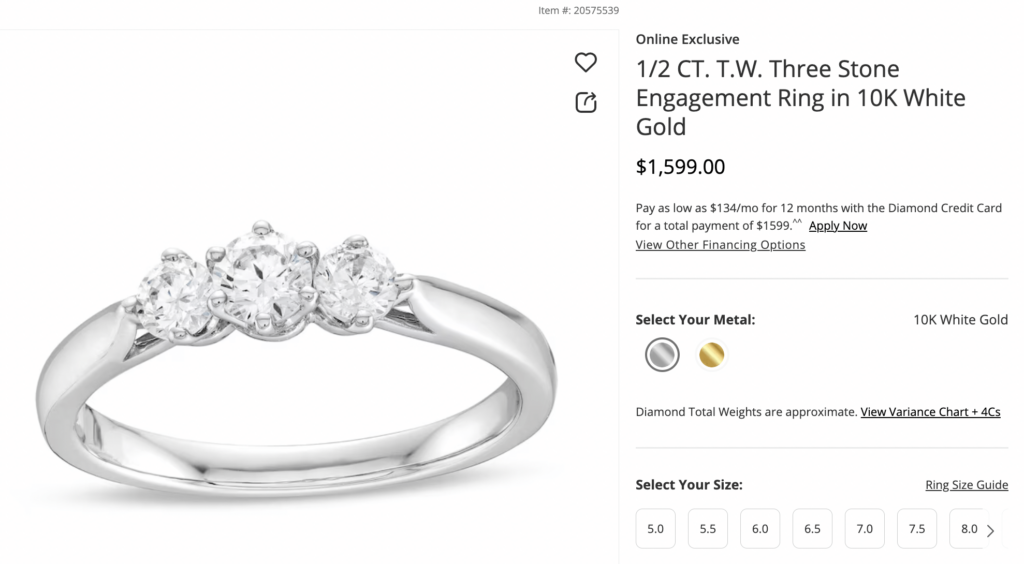
A comparable ½ carat engagement ring with three larger stones from Zales costs $1,599:
Likewise, this 1-carat composite diamond necklace is on sale for $1,728.35 vs. this 1-carat diamond necklace with a solitaire diamond pendant for $2,443.35:


Both are set in 14k yellow gold.
Fools diamond
A “fool’s diamond” is just another name for a fake diamond, or diamond simulant. People may also refer to diamond simulants as imitation diamonds.
Replica / travel diamond
Some people choose to purchase a fake diamond version of their natural diamond engagement ring to wear while traveling or exercising at the gym as a precaution against theft or damage.
Some people also choose to wear silicon or rubber rings in place of their diamond rings when they are exercising or doing outdoor activities, like the ones in this set from Amazon for just $9.58:
What's the best diamond alternative?
In terms of durability and similarity to natural diamonds, lab diamonds are the best alternative for engagement rings and other fine jewelry and are available at about a fourth of the price of natural diamonds of the same size.
Moissanite is also a highly durable and less expensive imitation diamond, though its rainbow light is often fairly distinguishable from the white light of a lab or natural diamond.
How to tell if a diamond is real
If you aren’t sure whether a piece of jewelry you own contains a diamond or fake diamond, here’s how to tell if a diamond is real at home:
- Look for imperfections – Natural diamonds often contain small imperfections, called inclusions. Look for small indentations, fractures, dark spots, and cloud or needlelike formations inside and on the surface of the stone. Visible imperfections on moissanites or even lab diamonds are less common because they are created in a lab under controlled conditions.
- Reflection test – Diamonds reflect white light, while diamond simulants like moissanite and cubic zirconia give off a distinct rainbow color when exposed to natural or artificial light.
- Water test – Diamonds are denser than water and will sink to the bottom of a cup filled with water. Cubic zirconia and moissanite stones typically do not sink unless they are particularly large and heavy. For this test to be most effective, you will have to remove the stone from its setting, since gold and silver also sink and may weigh down any stone set in them.
- Fog test – Diamonds are good heat conductors, so if you breathe on one closely, any fog formed should clear up quickly. However, this is also true of moissanites.
- Dot test or newspaper test – The idea behind this test is that a diamond’s high refractive index will prevent you from seeing or reading text or a drawing behind it. You can either place the loose gemstone flat side down on top of text in a newspaper or book, or draw a dot on a piece of paper smaller than the size of the stone. If you can see the text or dot through the stone, it is likely not a diamond. This test is not foolproof, however, since moissanites also have a high refractive index, and you may still be able to see text through a diamond that isn’t perfectly cut.
- Heat test – Fake diamonds cannot tolerate changes in heat the way a real diamond can. Only perform this test if you are OK with damaging a non-diamond stone. Place the stone on a fireproof surface or hold it with tweezers, then hold a lighter over the stone for 30-45 seconds. Immediately after, drop the stone into a cold glass of water. Real diamonds will sink to the bottom, while stones like cubic zirconia will likely shatter. However, moissanite has a higher level of heat resistance than a diamond and would pass this test.
- Scratch test – As the quality of cubic zirconia and moissanite stones have improved, this test has become less effective. It involves scraping the stone in question against a mirror, stone, or glass to see if it leaves a scratch mark. However, this test can damage your stone, even if it is a diamond.
Note that a lab diamond will also pass most of these tests because it is compositionally the same as a natural diamond.
The most effective way to determine if a diamond is real is to bring it into a professional jeweler who can examine and test it. You can also get a lab report from a professional organization like the Gemological Institute of America.
There are also at-home diamond testing tools you can purchase, like this testing kit from Amazon for $23.39:
Are fake diamonds worth anything?
While they do not hold their value as well as natural diamonds, “fake diamonds” like moissanite and cubic zirconia can be sold on consignment or through sites like ebay, Craigslist, or Facebook Marketplace. However, you shouldn’t expect to make close to what you initially paid for them.
Answers to FAQs about fake diamond vs real diamonds
What are fake diamonds called?
Fake diamonds are called diamond simulants because they simulate the look of a real diamond.
What is a good fake diamond called?
Moissanite and cubic zirconia are popular diamond simulants available at a fraction of the cost of natural and even lab-grown diamonds.
What is the meaning of simulated diamond?
Also called imitation diamonds, simulated diamonds are gemstones that look similar in appearance to a diamond but are compositionally different.
What is simulated moissanite?
Moissanite is a rare, naturally occurring mineral made of silicon carbide. However, most moissanite sold today is created in a lab as a diamond simulant.
How can you tell if a diamond is real?
The best way to determine if a diamond is real at home is to look for visible inclusions like dark marks, hairline fractures, or needle-like inclusions. Also, if you hold a diamond up to light, you should see mostly white light reflected, while diamond simulants like moissanite and cubic zirconia reflect rainbow light.
However, the only foolproof way to determine if a diamond is real is to take it into a professional jeweler or send it to a lab like GIA to have it evaluated.
Do fake diamonds shine?
Some diamond stimulants shine even more than traditional mined diamonds — moissanite, for example, is doubly refractive and has a higher refractive index than a diamond. However, a diamond’s shine is unique in that it reflects white light, rather than rainbow light like other diamond lookalikes.
Bottom line: Are fake diamonds worth it?
If you are shopping for a less expensive alternative to a natural diamond, lab-grown diamonds and diamond simulants like moissanite are highly durable and similar in appearance to natural diamonds, at least to the untrained eye. However, cubic zirconias, while extremely affordable, often lose their luster within about two years and will need to be regularly replaced.
If your partner doesn’t have their heart set on a diamond, a ring with a diamond simulant or lab-grown diamond may be the best option if you are limited on funds or want to be able to purchase a larger stone than you could afford as a natural diamond.
However, if you are looking for an investment piece, neither natural diamonds nor diamond simulants are a good choice. Unlike precious metals like gold and silver, diamonds are only worth about 50% of their initial purchase price on the resale market, and fake diamonds like moissanite are worth even less. Cubic zirconia is worth virtually nothing, unless you can find an independent buyer who likes the jewelry it’s set in.
If you do have a diamond to sell, A+ BBB-rated DiamondsUSA accepts all sizes of natural and lab-grown diamonds and offers a highest price guarantee.
SOURCES
- “The History of the Diamond as an Engagement Ring,” American Gem Society. https://www.americangemsociety.org/buying-diamonds-with-confidence/the-history-of-the-diamond-as-an-engagement-ring/
- “Is There a Difference Between Natural and Laboratory-Grown Diamonds?” by Russell Shor for the Gemological Institute of America Inc. https://www.gia.edu/gia-news-research/difference-between-natural-laboratory-grown-diamonds
- “The Knot 2023 Real Weddings Study,” by The Knot Research & Insights Team. The Knot. https://www.theknot.com/content/wedding-data-insights/real-weddings-study
- “Diamond Color Chart: The Official GIA Color Scale,” Gemological Institute of America. https://4cs.gia.edu/en-us/blog/diamond-color-chart-official-gia-color-scale/



